Hope For Those Living With Obesity
Obesity is a disease that affects over 115 million Americans. It’s a national crisis driven by an epidemic that has spiraled out of control. Every community across the country is impacted by obesity. But there is hope.
What You Should Know About Obesity:
- It’s not a character flaw. It’s a disease, a complex disease.
- Losing weight and keeping it off is hard.
- Diet and exercise aren’t always enough.
- Where you live and genetics play a role.
- Obesity Impacts Everyone, Regardless of Weight.
- It’s not funny. The belittling treatment that children with the disease endure—from children and adults alike—can create scars that last a lifetime.

The Good News: There are Treatment Options
Learn more about what obesity is, and what types of treatments are available.
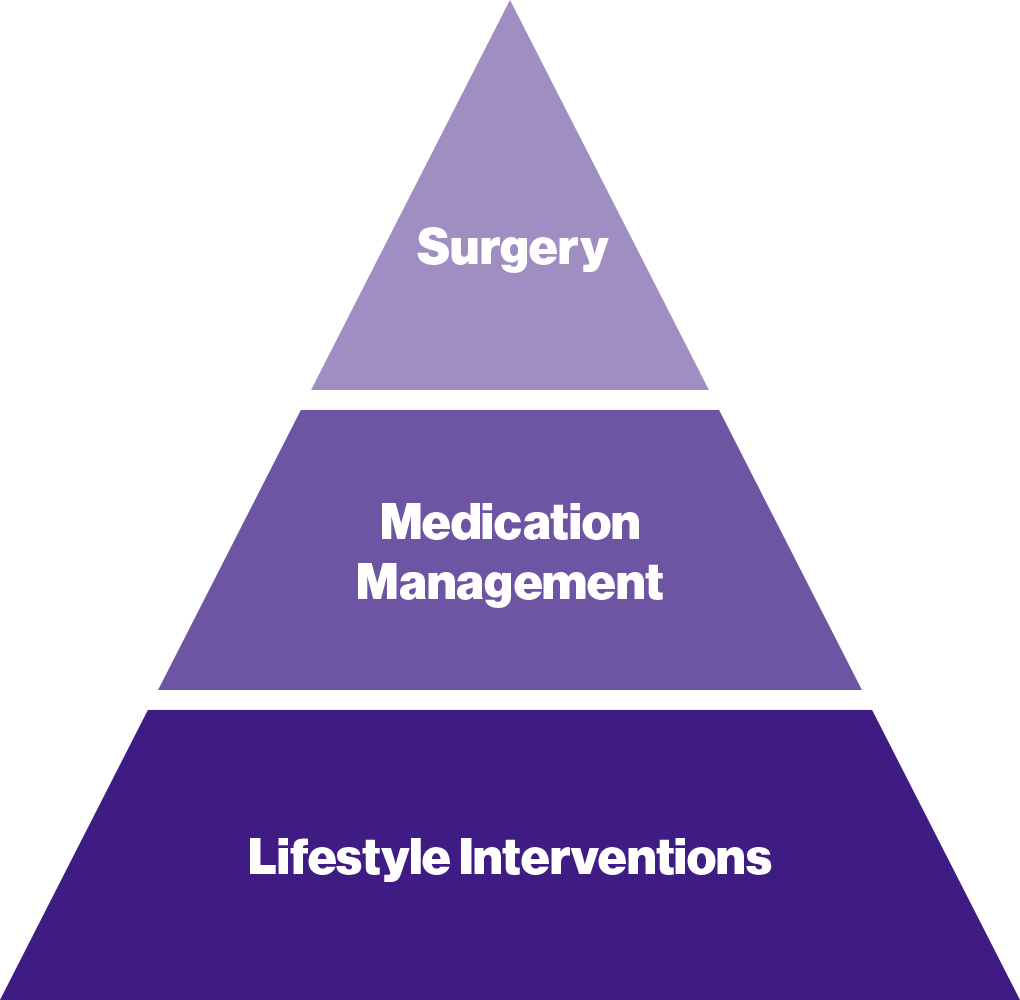
Treatment of obesity depends on disease severity. Available options include lifestyle interventions such as diet and physical activity, medications, and surgery for the more severe cases. If you think you have obesity, or are at risk, consult with your healthcare practitioner. If you have a BMI between 30 and 35, medication management may be the most appropriate option. For those with a BMI greater than 35 and two related metabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes and high lipids, surgery may be appropriate. Surgery may also be appropriate for those who have a BMI of 40 or over without any additional diseases. For children ages 2-19, you can learn more about the percentile ranges for each category in the section below.
The BMI Calculator and How to Use it
- Health professionals use a BMI Calculator to determine if you are at a healthy weight for your age and height. You can enter some basic information about yourself into Pennington Biomedical’s BMI Calculator to learn the following.
- BMI (Body Mass Index) is an estimate of body fat and is calculated for both children and adults. A high BMI might mean you are at a higher risk for diseases associated with obesity.
- The BMI Percentile is calculated for children and young adults aged 2 to 19. Health professionals can use the percentile score to categorize a child’s BMI to identify where the child falls in relation to other children of the same age and sex.
- BMI Z-Scores are also calculated for children and young adults aged 2 to 19. This number indicates how much higher or lower your BMI is on a standard growth chart. BMI Z-Scores help health professionals to monitor weight changes in children and adolescents especially if they are in the underweight or overweight percentiles.
| BMI Chart | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adults |
Ages 2-19 (Percentiles) |
|
| Under Weight | < 18.5 | < 5th |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 to < 25 | 5th to < 85th |
| Overweight | 25 to < 30 | 85th to < 95th |
| Obese (Class I) | 30 to < 35 | >= 95th |
| Obese (Class II) | 35 to < 40 | - |
| Obese (Class III+) | >= 40 | - |
About Obesity Treatment Options:
Medical Management: In carefully selected patients, appropriate drug or surgical treatment can help with weight loss. Weight loss medicines have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for both short- and long-term use. A person must be under continual medical supervision by a physician while taking such medicines. The medication and dosage are tailored individually to the patient.
Surgery: Surgical therapy such as gastric bypass or gastric banding may be considered for a limited number of individuals with obesity, who also have other chronic diseases such as high blood pressure, diabetes or sleep apnea, AND for whom dietary attempts at weight loss maintenance not been successful.
The American Academy of Pediatrics also recently updated their Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Obesity. Comprehensive treatment suggested by the American Academy of Pediatrics include nutrition support, physical activity treatment, behavioral therapy, pharmacotherapy, and metabolic and bariatric surgery.
For more information on metabolic and bariatric surgery options, visit the Metamor Institute, the first institute in the nation to offer an integrated and multidisciplinary approach to caring for individuals who suffer from these devastating diseases in a single facility at the world-renowned Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, LA.





